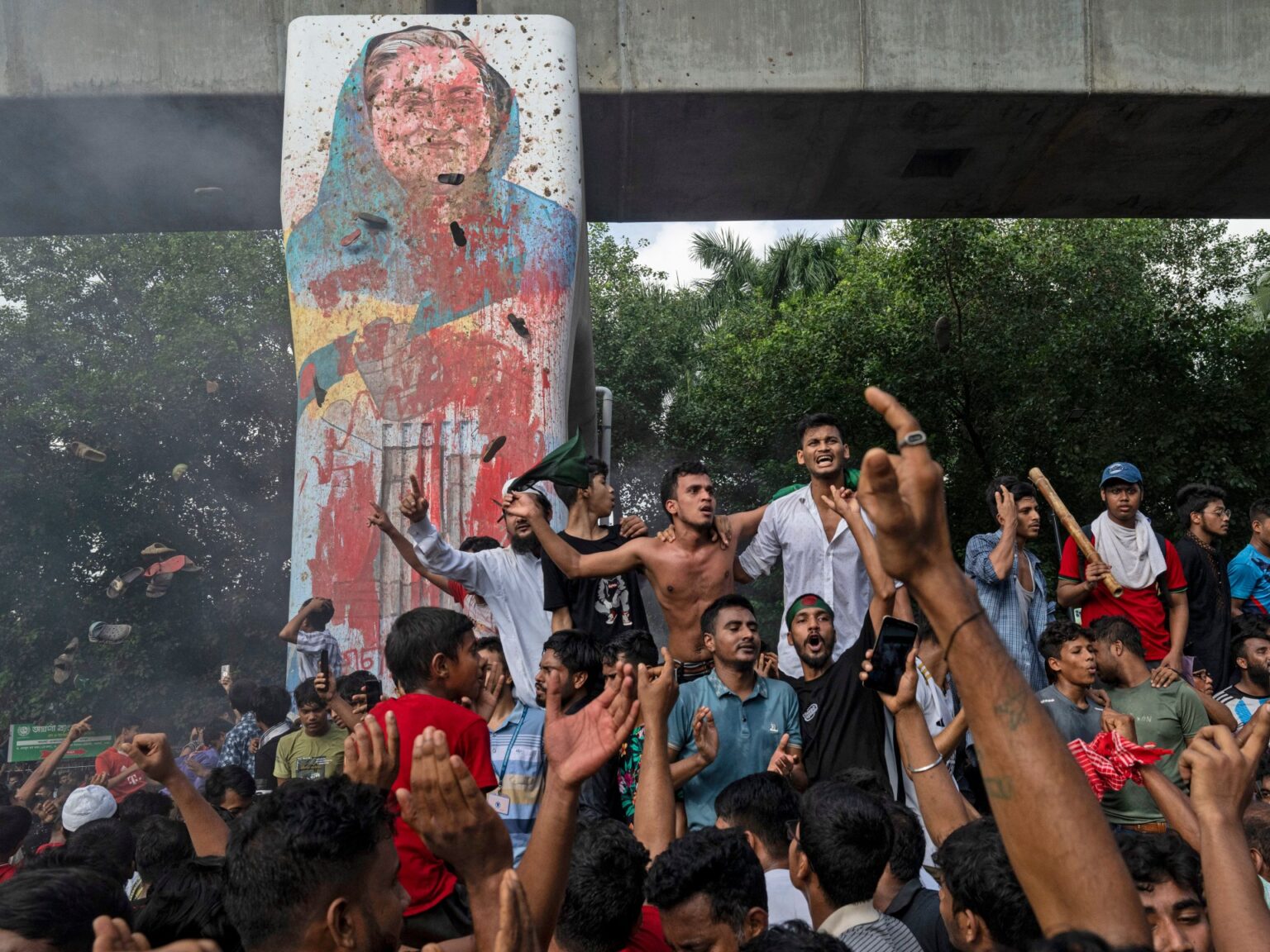For most of his adult life, Rafiul Alam did not believe that voting was worth the walk to the polling station. He is 27, grew up in a middle-class neighbourhood of Dhaka, and became eligible to vote nearly a decade ago. He never did – not in Bangladesh’s national elections in 2018, nor in the 2024 vote.
“My vote had no real value,” he said.
Like many Bangladeshis in his age group, Alam’s political consciousness formed under former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina’s long period of government, when opposition parties and election watchdogs repeatedly questioned the credibility of polls.
Over time, he said, disengagement with politics became normal, even rational, for a generation. “You grow up knowing elections exist, but believing they actually don’t have the power to decide anything. So you put your energy elsewhere… studies, work, even trying to leave the country,” he said.
This calculation began to shift for him in July 2024, when student protests over a government job reservation system favouring certain groups spiralled into a nationwide uprising. Alam joined marches in Dhaka’s Mirpur area and helped coordinate logistics for protests, as Hasina’s security forces launched a brutal crackdown.
The United Nations Human Rights Office later estimated that up to 1,400 people – most of them young – may have been killed before Hasina fled to India on August 5, 2024, ending nearly 15 years in power.
When Hasina left, Alam said the moment felt like something that had appeared permanent had broken. “For the first time, it felt like ordinary people could push for a change,” he said. “Once you experience that, you feel responsible for what comes next.”
Bangladesh is now heading for a national election on February 12, the first since the uprising. European Union observers have described the upcoming vote as the “biggest democratic process in 2026, anywhere”. And Alam plans to vote for the first time.
“I’m thrilled to exercise my lost right as a citizen,” he said.
He is not alone. Bangladesh has about 127 million registered voters, nearly 56 million of them between the ages of 18 and 37, according to the Election Commission. They constitute about 44 percent of the electorate, and are a demographic widely seen as the driving force behind Hasina’s downfall.
“Practically speaking, anyone who turned 18 after the 2008 parliamentary election has never had the chance to vote in a competitive poll,” said Humayun Kabir, director general of the Election Commission’s national identity registration wing.
“That means people who have been unable to vote for the last 17 years are now in their mid-30s… and especially eager to cast their ballots.”
This eagerness comes after three post-2008 elections that “were not considered credible”, Ivars Ijabs, the EU’s chief observer, said.
The 2014 polls saw a mass opposition boycott, and dozens of seats where Hasina’s Awami League party faced no contest. The 2018 vote, though contested, became widely known as the “night’s vote”, after allegations that ballot boxes had been filled before polling day.
The 2024 election, meanwhile, again went ahead amid a major boycott by opposition parties, with critics arguing that conditions for a “fair contest did not exist”.

A pivotal electorate
Fragmented by class, geography, religion and experience, Bangladesh’s young voters are united less by ideology than by a shared suspicion of institutions, which, for most of their adult lives, have failed to represent them, say analysts.
“There is a significant age gap between pre–Hasina regime voters and new voters,” said Fahmidul Haq, a writer and faculty member at Bard College in New York and a former professor at the University of Dhaka. “Because of the nature of elections under the Hasina administration, we do not know the actual level of public acceptance of the political parties.”
As a result, he said, the current cohort of first-time voters will play a decisive role in shaping the future direction of politics in Bangladesh. Haq described the upcoming election as a psychological release valve after years of repression, during which young people “could not hold their representatives accountable; rather, those representatives appeared to them as oppressors”.
Many young people still do not trust the existing system, Haq argued, and some remain sceptical of the democratic transition itself.
Umama Fatema, a Dhaka University student who emerged as a prominent leader during the 2024 protests, said the uprising generated powerful expectations among young people: promises of “no corruption, no manipulation, equality of opportunity and political reform”.
But translating these aspirations into institutions has proven far more difficult. As the transition unfolded, Fatema said the reform process, led by the interim administration of Nobel laureate Muhammad Yunus, alongside manoeuvring by political parties – including those born out of 2024’s protests – became increasingly complex.
“Very few people and their aspirations have been meaningfully involved and incorporated,” she said.
A fraught alliance
With the Awami League barred from political activity by the interim Yunus government, the election has turned into a battle between two rival coalitions: one led by the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP), and the other by Jamaat-e-Islami.
For many young protesters, this outcome cuts against the spirit of 2024.
Pantho Saha, a 22-year-old student from the Cumilla district in the country’s southeast, said many with whom he protested in 2024 had hoped the leaders who emerged from the uprising would break what he described as the “same old dynastic” patterns.
That expectation began to fracture, he said, when the National Citizen Party (NCP), a youth-led formation born out of the protest movement, moved towards an electoral alliance with Jamaat-e-Islami. A far-right Islamist party, the Jamaat’s opposition to Bangladesh’s independence during the 1971 war has long limited its mainstream appeal.
“Historically, those who rule us come to power with big promises,” Saha said. “But after a few years, power blinds them, and the same abuses repeat.”
The NCP, he said, initially felt different. “We thought of the NCP as a beacon of light. But seeing it align with a party that carries so much historical baggage made many of us lose hope.”
Fatema, who led the protests alongside several figures who later founded the NCP, said the party’s alignment with the Jamaat risks shrinking the significance of the July 2024 uprising. “Over time, it could seriously damage how this uprising is remembered in history,” he warned.
The NCP positioned itself at its launch as a generational alternative to Bangladesh’s traditional parties, promising what it called a “new political settlement” rooted in the 2024 July movement. But as talks advanced over the electoral alliance with Jamaat-e-Islami, the party saw a wave of resignations, including from several senior figures and women leaders who had been expected to contest parliamentary seats. Many of them have since announced independent bids, saying the party was “drifting from its founding commitments”.
Nahid Islam, the NCP’s chief, has defended the alliance with Jamaat-e-Islami, describing it as a “strategic electoral arrangement aimed at greater unity”, rather than an ideological alignment.
Between hope and politics
Even so, the February 12 ballot carries particular weight for many younger Bangladeshis who helped drive last year’s uprising.
Moumita Akter, 24, a master’s student at Chittagong University who took part in the anti-Hasina protests, described the vote as “the first step to restore at least the most basic democratic practices”.
“I don’t expect miracles from a single vote. But I want to see whether the system can at least function properly. That alone would be a major change,” she said.
For others, like Sakibur Rahman, 23, a voter from the eastern Brahmanbaria district who studies philosophy at the University of Dhaka, the appeal of democracy remains conditional.
“You can talk about democracy all day, but if people don’t feel safe, can’t speak freely and can’t earn a living, democracy feels abstract, he told Al Jazeera.
Rahman said he would support whichever party could credibly guarantee public safety, freedom of expression, religious freedom, and minorities living without fear.
For many women voters, the calculation is sharper still. Women make up nearly half of Bangladesh’s electorate, but young women say questions of dignity and everyday security will shape their ballot.
“We hear promises of women’s rights, but the lived reality is far from ideal. That will shape how many of my female friends will vote,” Akter, the master’s student, said.
Yet the political field they are being asked to choose from remains overwhelmingly male. Election Commission data shows that only 109 of the 2,568 candidates contesting the election, or about 4.24 percent, are women.
Fatema said the political space for women has narrowed rather than expanded since the uprising. “After August 5, women who speak about their agency, their contributions, and their right to representation have been suppressed in many ways,” she said.
“Harassment, from online abuse to sexual threats, has become routine in political spaces.” These pressures are pushing women out of visible political roles, just as the country enters a critical political transition, she added.
Mubashar Hasan, a political observer and adjunct researcher at Western Sydney University’s Humanitarian and Development Research Initiative, said the disconnect between women’s prominence in protest movements and their marginalisation in formal politics raises doubts about the depth of reform.
“No structural change is possible without women’s political representation, and participation at the highest levels… both in parliament and in policymaking,” he said. “Without that, promises of any new political order remain incomplete.”
Fahmidul Haq of Bard College said political parties would have to approach young voters differently than in the past, by addressing “their traumas, desires, and demands sincerely”, and by campaigning with honesty and transparency.
“Young people are deeply sceptical of absurd promises,” he said, adding that those may in fact alienate them.
Still, something fundamental has changed. For Alam, the first-time voter from Dhaka’s Mirpur, July 2024 permanently altered how his generation relates to power.
“We now dare to question everyone,” he said. “Whoever comes to power, that habit won’t disappear.”
https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2026/1/20/bangladeshi-youth-toppled-hasina-now-they-could-decide-next-prime-minister?traffic_source=rss