Venezuela is ready to carry a referendum on Sunday on whether or not to ascertain a brand new state in a disputed, oil-rich territory lengthy dominated by Guyana.
The vote comes after the International Court of Justice (ICJ) urged Venezuela to chorus from “taking any action” that would alter the established order within the area. However, it didn’t particularly ban Caracas from holding the referendum as Guyana had requested.
Friday’s ruling is the most recent improvement within the bigger border dispute. The ICJ mentioned in April that it had jurisdiction over the case however a last ruling might be years away.
Here is what to know in regards to the vote and the dispute.
A referendum in Venezuela
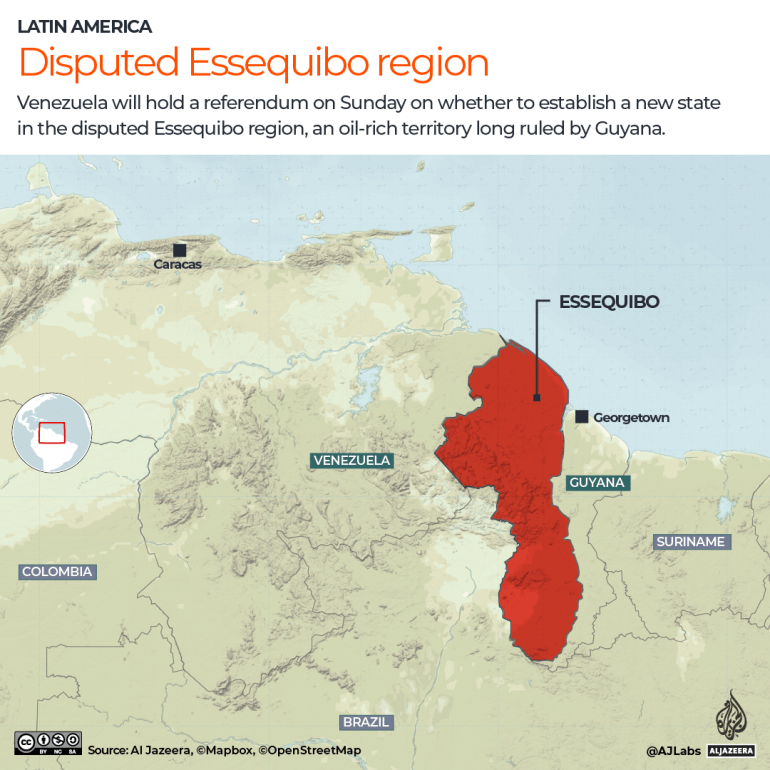
Venezuela will go forward with a referendum on December 3, over its rights to a probably oil-rich territory that’s the topic of a border dispute with Guyana.
The referendum will ask Venezuelans 5 questions, together with in the event that they agree with creating a brand new state known as Guayana Esequiba within the Essequibo area, granting its inhabitants Venezuelan citizenship in addition to id playing cards and incorporating that state into the map of Venezuelan territory.
Guyana fears that the referendum might be a pretext for a land seize. “The collective decision called for here involves nothing less than the annexation of the territory in dispute in this case,” Paul Reichler, an American lawyer representing Guyana, instructed the ICJ. “This is a textbook example of annexation.”
The Venezuelan authorities has not defined how it could create the state ought to voters approve it. The referendum can be described as consultative.
However, the ICJ mentioned there was a “serious risk of Venezuela acquiring and exercising control and administration of the territory in dispute in the present case”.
Political analysts anticipate voters to approve the proposal, given the dearth of any “no” marketing campaign and the probability that voters who’re opposed will keep residence.

Dispute between Venezuela and Guyana
Caracas considers Essequibo as its personal as a result of the area was inside its boundaries in the course of the Spanish colony.
The Guyanese authorities insists on retaining the border decided in Paris in 1899 by an arbitration panel, whereas claiming that Venezuela had agreed with the ruling till it modified its thoughts in 1962.
Caracas claims that the Essequibo River to the area’s east kinds a pure border and has been recognised as such since 1777.
It dismisses the 1889 ruling. During these negotiations, the United States represented Venezuela on the panel partly as a result of the Venezuelan authorities had damaged off diplomatic relations with the United Kingdom.
Venezuelan officers contend that the Americans and Europeans conspired to cheat their nation out of the land and argue {that a} 1966 settlement to resolve the dispute successfully nullified the unique arbitration. Guyana maintains that the preliminary accord is authorized and binding.
Friction between the nations has elevated since 2015 on account of oil exploration operations by ExxonMobil and different firms in offshore areas intersecting the disputed territory.
The Venezuelan authorities maintains that Guyana doesn’t have the correct to grant concessions in maritime areas of the Essequibo.

The relevance of the Essequibo
The territory bigger than Greece, often known as “The Essequibo,” quantities to greater than two-thirds of the territory of Guyana and is residence to 125,000 of its 800,000 residents.
The 159,500sq km (61,600sq-mile) space is situated within the coronary heart of the Guiana Shield, a geographical area within the northeast of South America and one of many 4 final pristine tropical forests on the earth mined with pure and mineral sources, together with giant reserves of gold, copper, diamond, iron and aluminium amongst others.
The area additionally has the world’s greatest reserves of crude oil per capita. Just final month, Guyana introduced a “significant” new oil discovery, including to estimated reserves of no less than 10 billion barrels – greater than Kuwait or the United Arab Emirates.
With these sources, the nation is ready to surpass the oil manufacturing of Venezuela and by 2025, in line with projections, the nation is on observe to change into the world’s largest per-capita crude producer.
Exxon and its companions – the US-based Hess Corp and China’s CNOOC – are the one lively oil producers in Guyana. Their initiatives are anticipated to succeed in 1.2m barrels per day of output by 2027, turning Guyana into one in all Latin America’s most outstanding producers, solely surpassed by Brazil and Mexico.
International reactions
Brazil’s high diplomat for Latin American affairs, Gisela Maria Figueiredo, mentioned on Thursday that President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva’s administration was following the scenario with “concern”.
In the US, which has shut relations with Guyana, National Security Council spokesman John Kirby appealed for a peaceable decision to the dispute.
Analyst Rocio San Miguel of the Citizen Watchdog on Security, Defense and the Armed Forces mentioned that whereas Venezuela has considerably extra army energy than Guyana, it could not be capable of stand as much as Guyana’s allies, which embrace the US.
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2023/12/3/venezuela-holds-referendum-on-oil-rich-guyana-region-four-things-to-know?traffic_source=rss


